A battery breaker plant is a facility that is used to recycle batteries by breaking them down into their component parts. The process typically involves crushing the batteries to separate the different materials, such as lead, acid, and plastic, which can then be processed further and reused in the production of new batteries or other products. Battery breaker plants are an important part of the recycling industry, as they help to reduce the environmental impact of battery production and disposal by conserving resources and reducing the amount of waste that ends up in landfills.
How a battery breaker works
Lead Batteries contain various materials that can be considered as hazardous waste if not properly disposed, such as lead, acid(electrolyte), and plastic. A battery breaker is specifically designed to safely and efficiently extract these materials from the spent battery and prepare them for the reuse.
The process of breaking a battery typically involves a crushing session to separate the different materials from the spent lead battery body, which can then be further processed and purified. The purified materials can, then, be reused in the production of new lead batteries or other products, reducing the need for virgin raw materials from the nature and minimizing the waste formation.
Lead acid batteries are commonly composed of two plates: one made of Pb alloy and the other one of PbO2. During batteries’ discharging, the PbSO4 is formed. The PbO2 plate is essentially composed of a Pb alloy grate in which a PbO2 paste is impregnated. The grates are normally composed of alloys containing a low amounts of Ca, Sb and Sn.
A polypropylene box typically contains the electrolyte and a group of six cells, where the electrolyte is based on a sulfuric acid solution.
Lead acid battery recycling is very similar to the primary lead production process. The main differences are concerning the material preparation before reduction, which affects plant size, since there is no need for sintering.
The recycling sequential steps normally are: separation of the plastic case (using hammers or saws), acid removal, separation of the plastic, metallic lead and paste separation, reduction, refining and casting. Acid, polypropylene and lead are recovered in the recycling process.
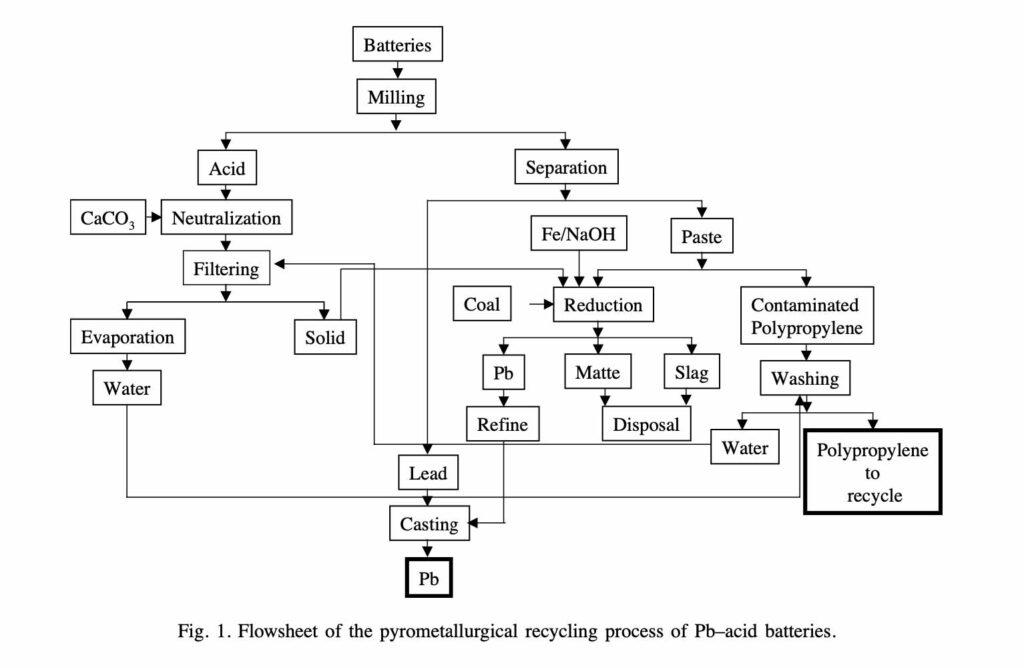
Source: Espinosa et al./Journal of Power Sources 135 (2004) 311–319
What is the Battery breaker unit capacity
The capacity of a battery breaker unit refers to the amount of batteries designed to be processed in a given period of time. This capacity can widely varies depending on the size and design of the unit, as well as the type of batteries intended to be recycled. Battery breaker units can be designed to handle a few hundred batteries per hour, while others may be capable of processing several thousand batteries per hour.
The capacity of a battery breaker unit can be expressed in different ways, such as the number of batteries processed per hour, the volume of batteries that the unit can hold or the weight of the batteries that can handle. In general, the majority of the battery breaker units use this last option and tipycally expressed in Tons per hour, means, Tons of scrap batteries handled in an hour. Based on these differentations, the Battery breaker unit may has a higher or lower capacity rate. In some cases the ratio capacity/unit size may be confusing but this is because some units may be designed for high-volume with continuous operation (24 hours), while others may be suitable to a smaller-scale with intermittent operation.
How does battery recycling work?
Battery recycling involves a series of steps to safely and effectively extract the valuable materials from used batteries and prepare them for the reuse. The specific process may vary depending on the type of battery being recycled and the equipment or technology used by the recycling facility. Here is a general overview of the main steps involved in the battery recycling:
- Collection: Used batteries are collected from various sources, such as consumers, businesses, and industrial facilities.
- Sorting: The batteries are sorted by type, size, and condition to ensure that they are processed in the most efficient and effective way.
- Disassembly: The batteries are disassembled to remove any external components, such as insulation, terminals, and labels, which are often made of plastic or other non-metallic materials.
- Crushing: The batteries are then crushed to break them down into smaller pieces, which makes it easier to separate the different materials.
- Separation: The crushed batteries are then subjected to various physical and chemical processes to separate the different materials, such as lead, acid, and plastic.
- Purification: The separated materials are then purified and cleaned to remove impurities and contaminants.
- Reuse: The purified materials are then prepared for reuse in the production of new batteries or other products.
Overall, battery recycling helps to conserve resources, reduce pollution, and reduce the environmental impact of battery production and disposal.
Comments are closed.

